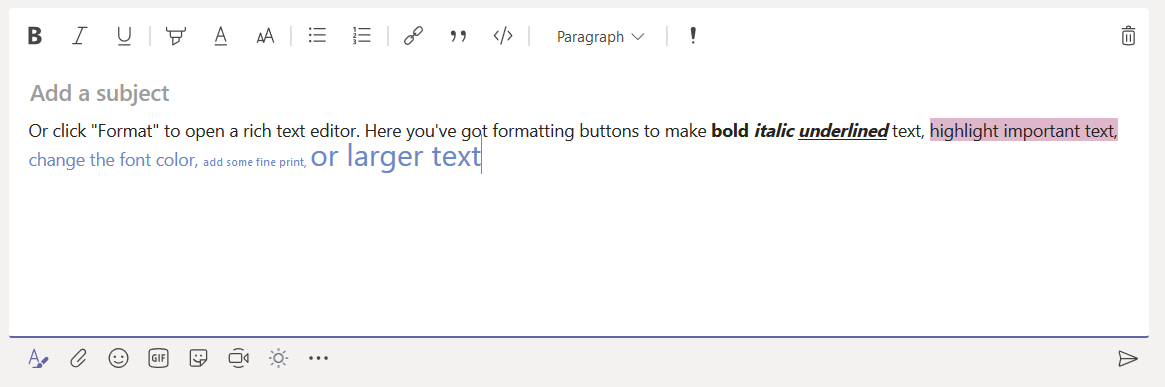
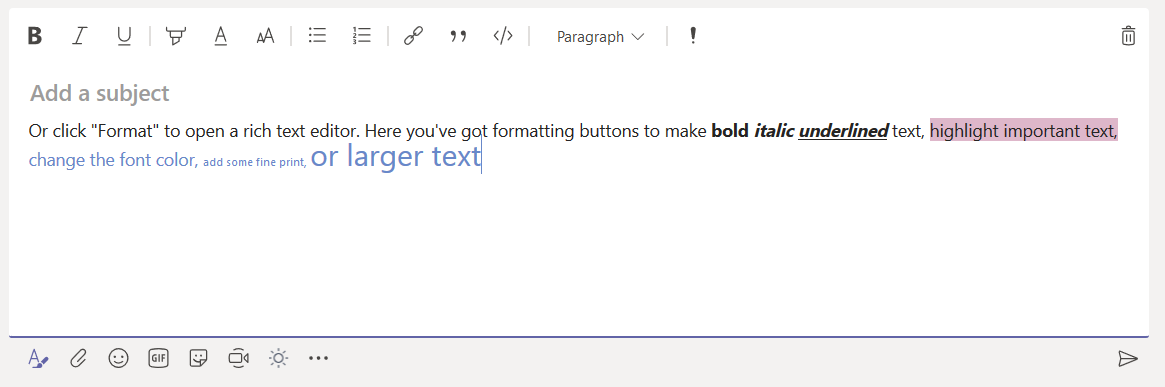
While hosting a bot on the Azure network allows you to use pre-built solutions or develop a bot without purchasing dedicated hardware, the bots we’ve deployed thus far do not have access to internally-housed data. And program execution can be slow (expensive, or a combination of the two) depending on the chosen pricing plan. But you can build an Azure bot that is essentially a proxy to a self-hosted bot.
This means you can host the bot on your private network (it needs to be accessible from the Azure subnets) and access internal resources from your bot code. Obviously, there are security implications to making private data available via an Azure bot – you might want to implement user authentication to verify the bot user’s identity, and I wouldn’t send someone their current credit card information over a bot even with authentication.
How to Communicate with a Self-hosted Bot from Azure:
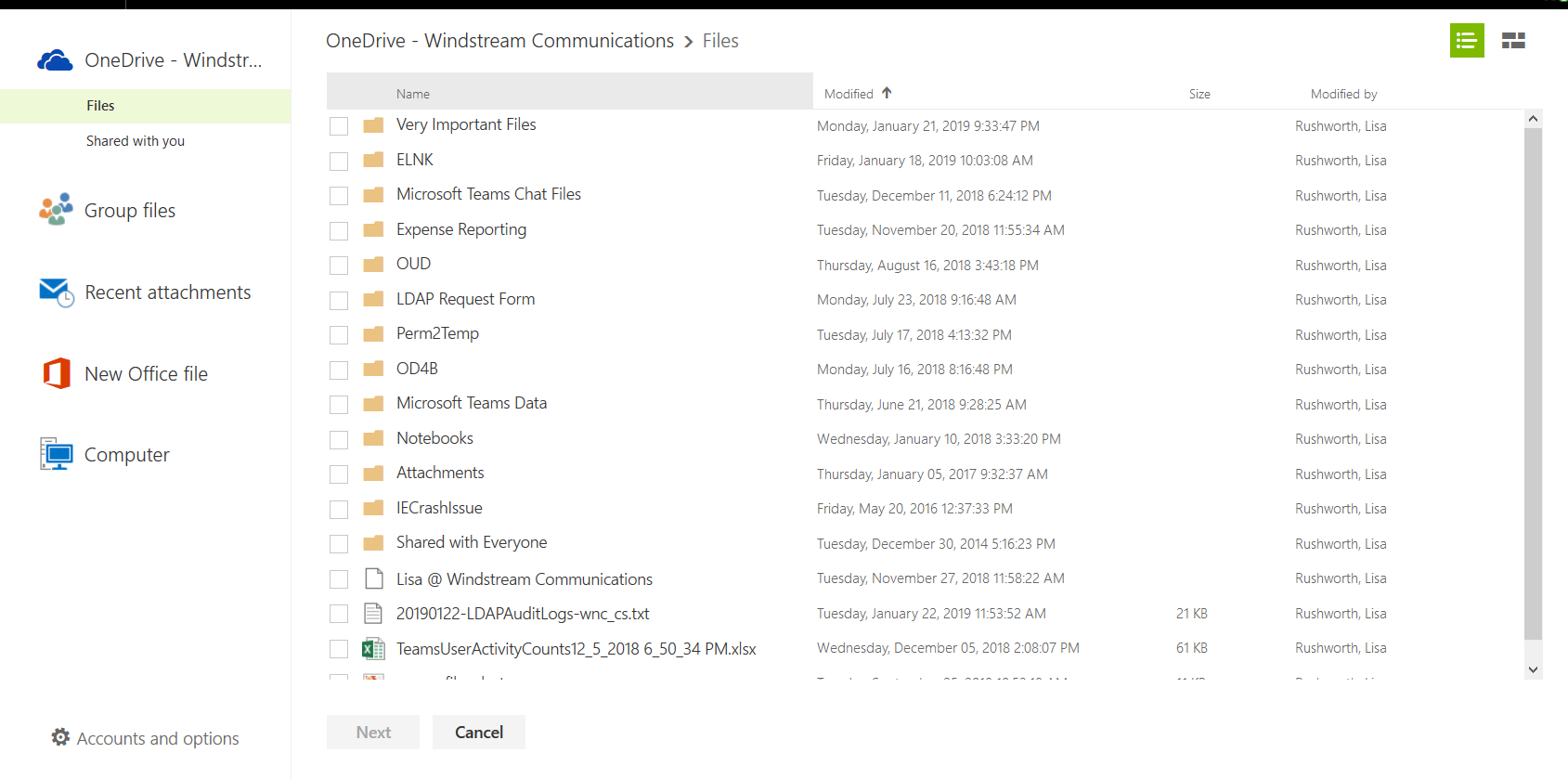
Register an Azure bot. From https://portal.azure.com, select “Create a resource”. Search for “bot” and select “Bot Channels Registration”.
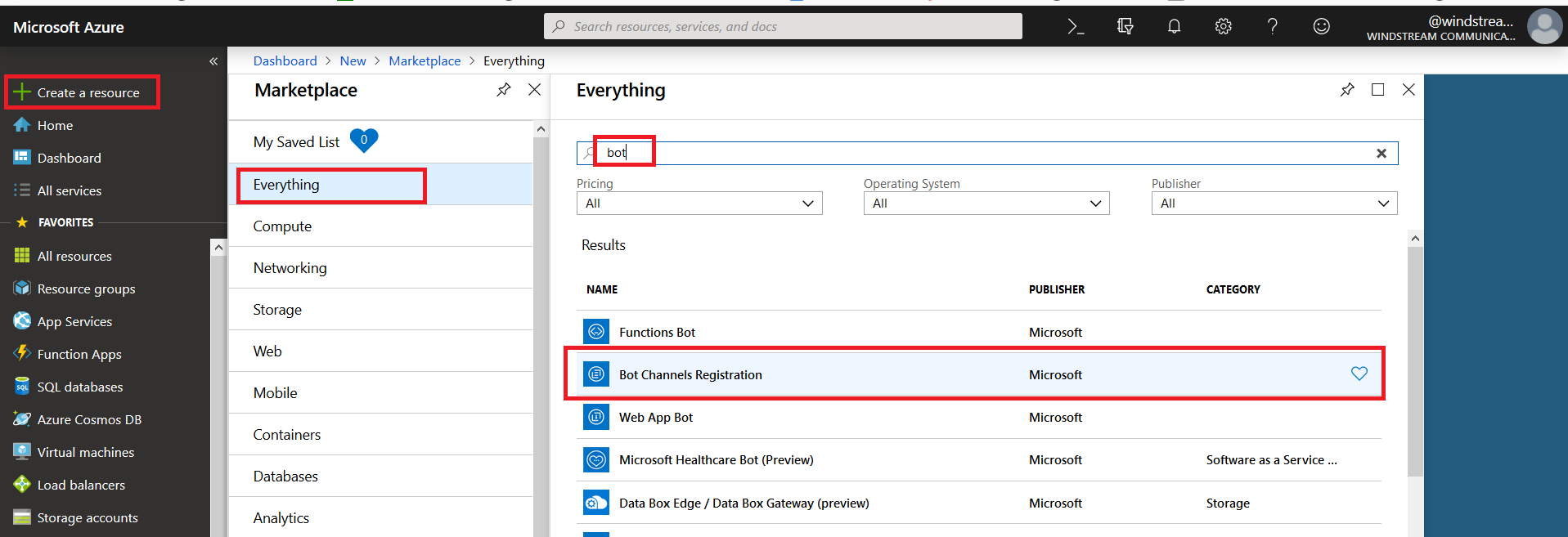
On the pane which flies out to the right, click “Create” (if you will be deploying multiple self-hosted bots to Azure, click the little heart so you can find this item on “My Saved List” when creating a new resource).
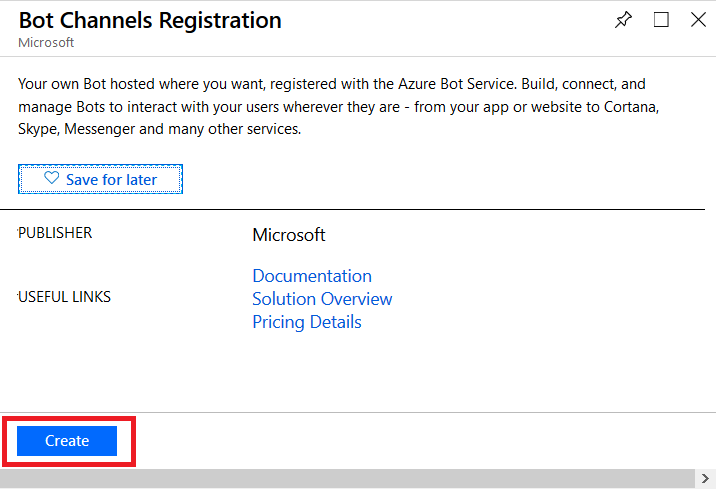
Provide a unique name for your Azure bot. If you have not yet created a resource group, you will need to create one. Make sure the hosting location is reasonable for your user base – East Asia doesn’t make sense for something used on the East coast of the US!
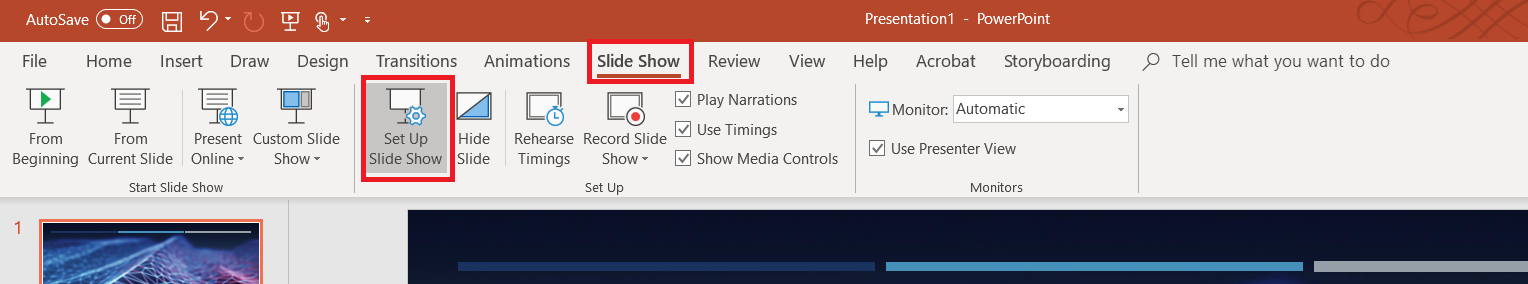
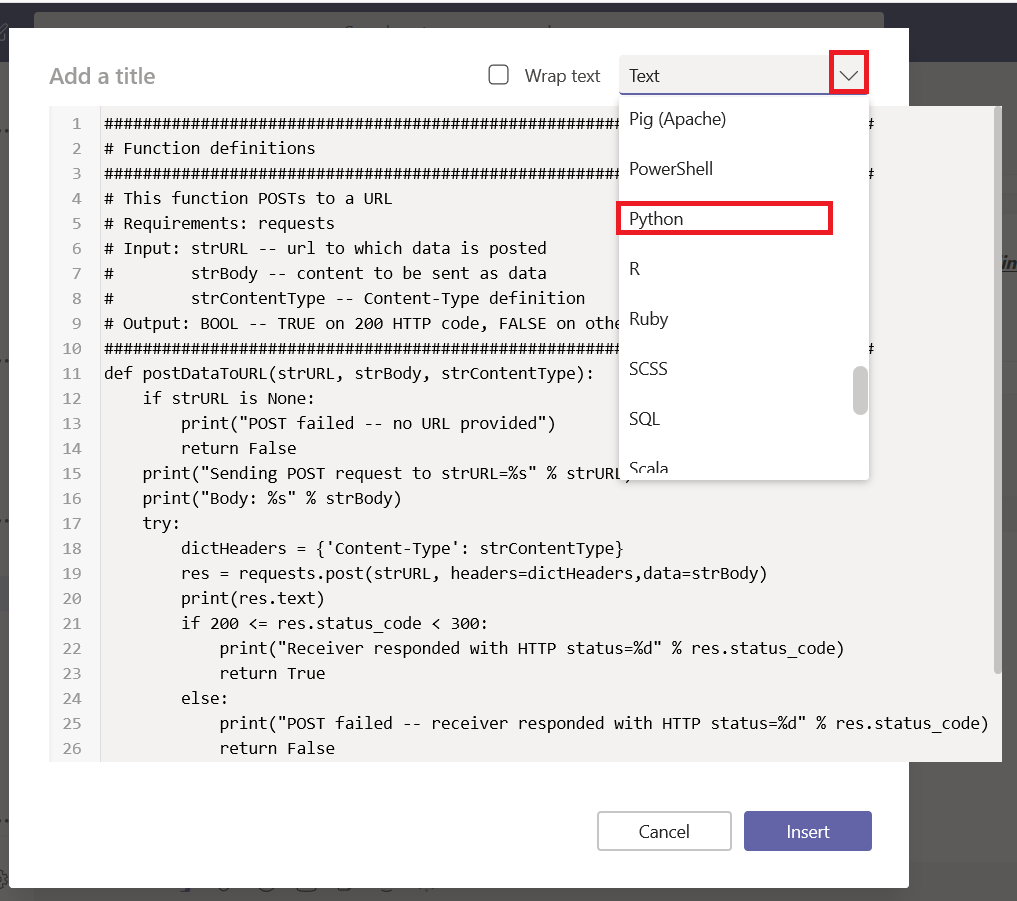
Select the pricing tier you want – I use F0 (free) which allows unlimited messages in standard channels (Teams, Skype, Cortana) and 10,000 messages sent/received in premium channels (direct user interaction … which I specifically don’t want in this case). Then provide the endpoint URL to interact with your locally hosted bot.
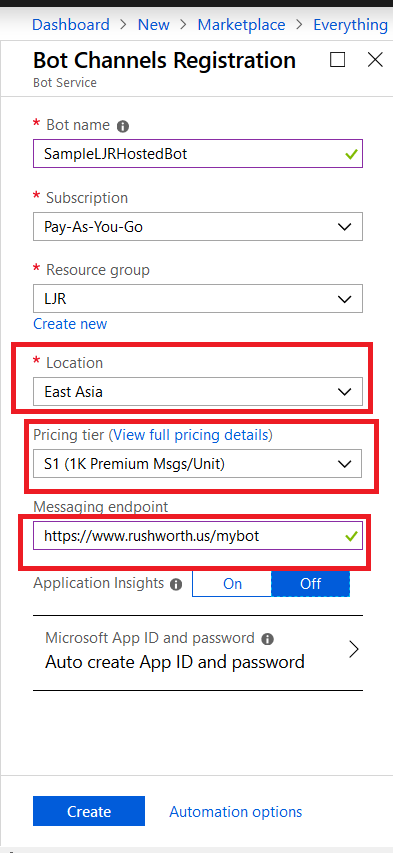
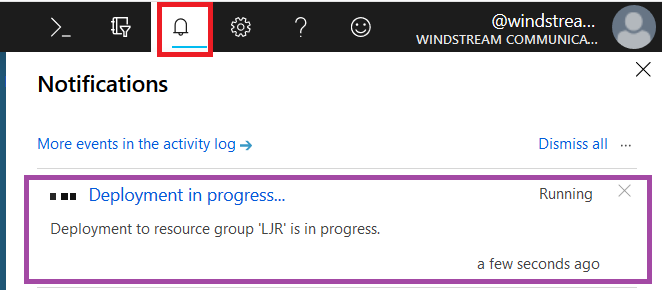
Click “Create” and Azure will begin deploying your new resource. You can click the “Notifications” bell icon in the upper right-hand portion of the page to view deployment progress.
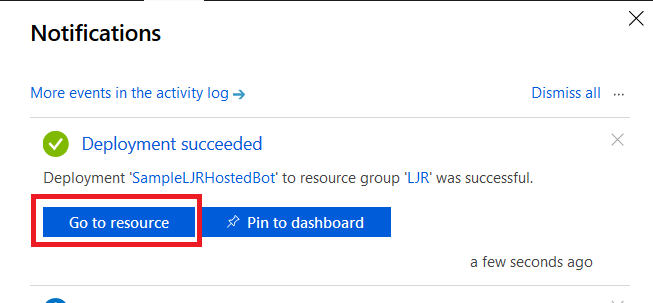
When deployment completes, click “Go to resource” to finish configuring your Azure bot.
Select “Settings” from the left-hand navigation menu, then find the application ID. Click “Manage”.
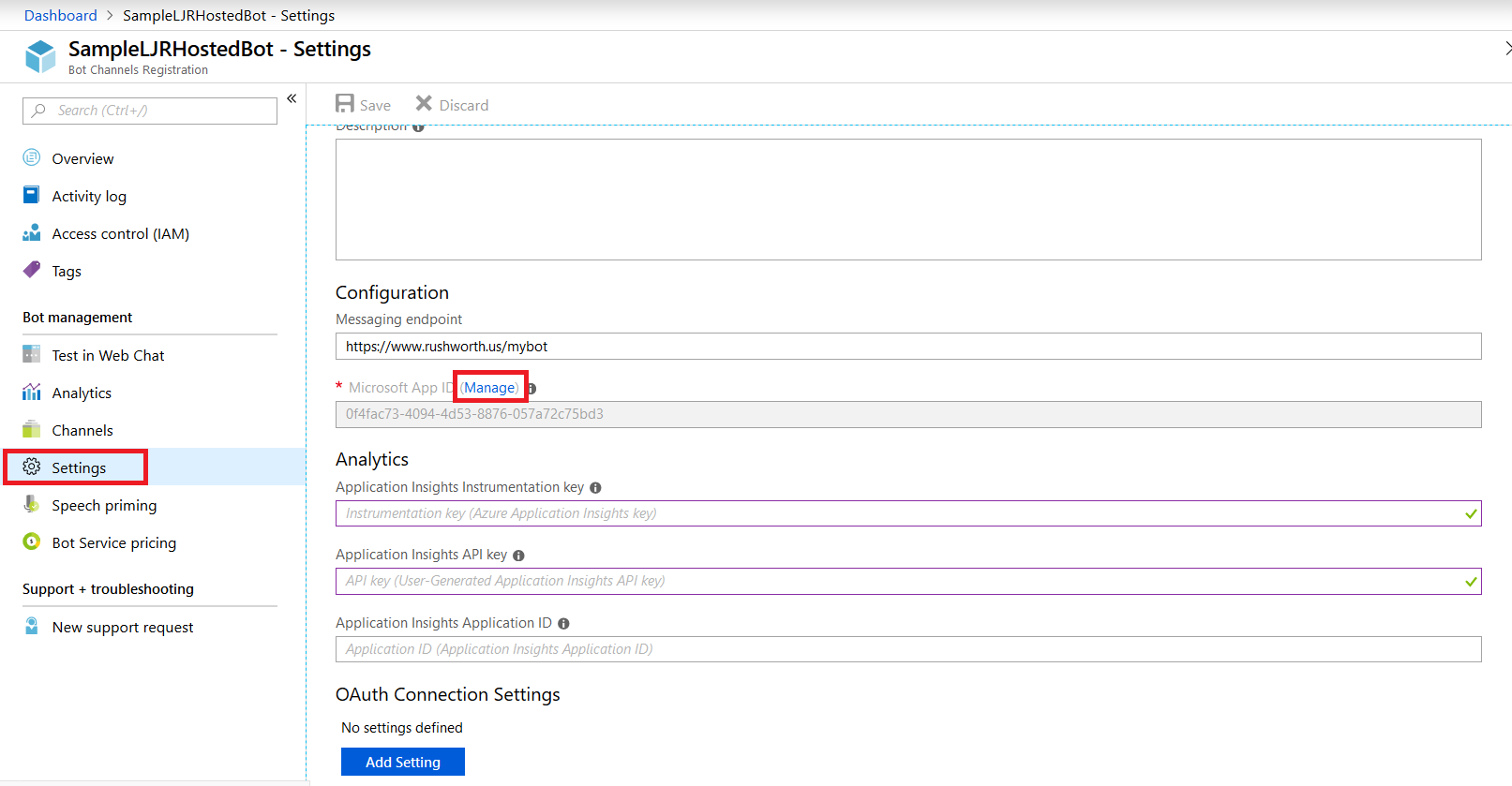
This will open a new portal – you may be asked to sign in again. You are now looking at the application registration in Microsoft’s developer application registration portal. There’s already an application secret created but beyond the first few letters … what is it? No idea! I’m a cautious person, and I don’t know if MS has embedded this secret somewhere within the bot resource. Since an application can have two secrets simultaneously, I do not delete the automatically-created secret and click “Generate New Password”.
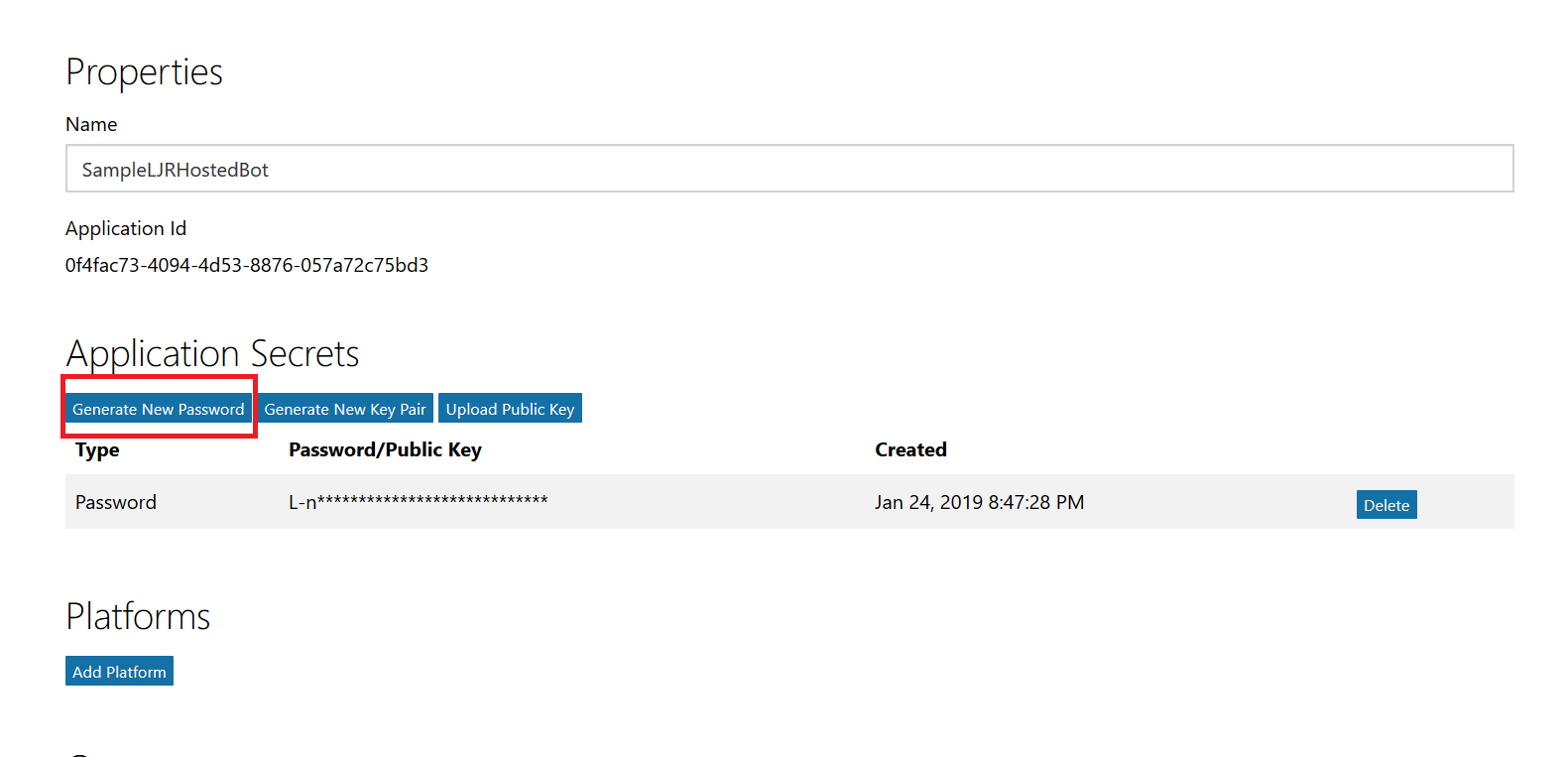
A new pane will appear with your new secret – no, the one in the picture isn’t real. Copy that and store it somewhere – you’ll need to add it to your bot code later.
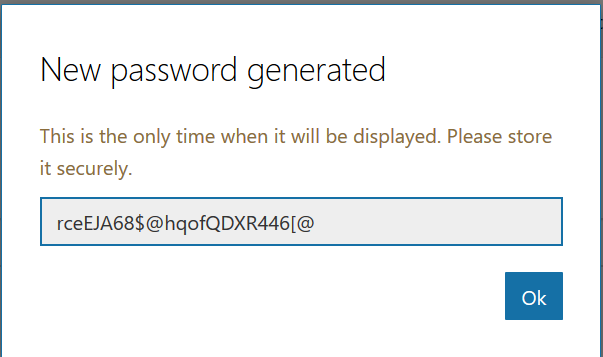
Close the application registration tab and return to the Azure portal tab. Click on “Channels” in your bot and add channels for any interactions you want to support. In this case, I want to publish my bot to Teams. There aren’t really settings* for teams – just click to create the channel.
* You can publish a bot to the Microsoft App Source … but is your bot something that should be available to the Internet at large? It depends! If you’re writing a bot to provide enterprise customers another support avenue, having the bot available through App Source makes sense. If you’re creating a bot to answer employee-specific questions, then you probably want to keep the bot out of App Source
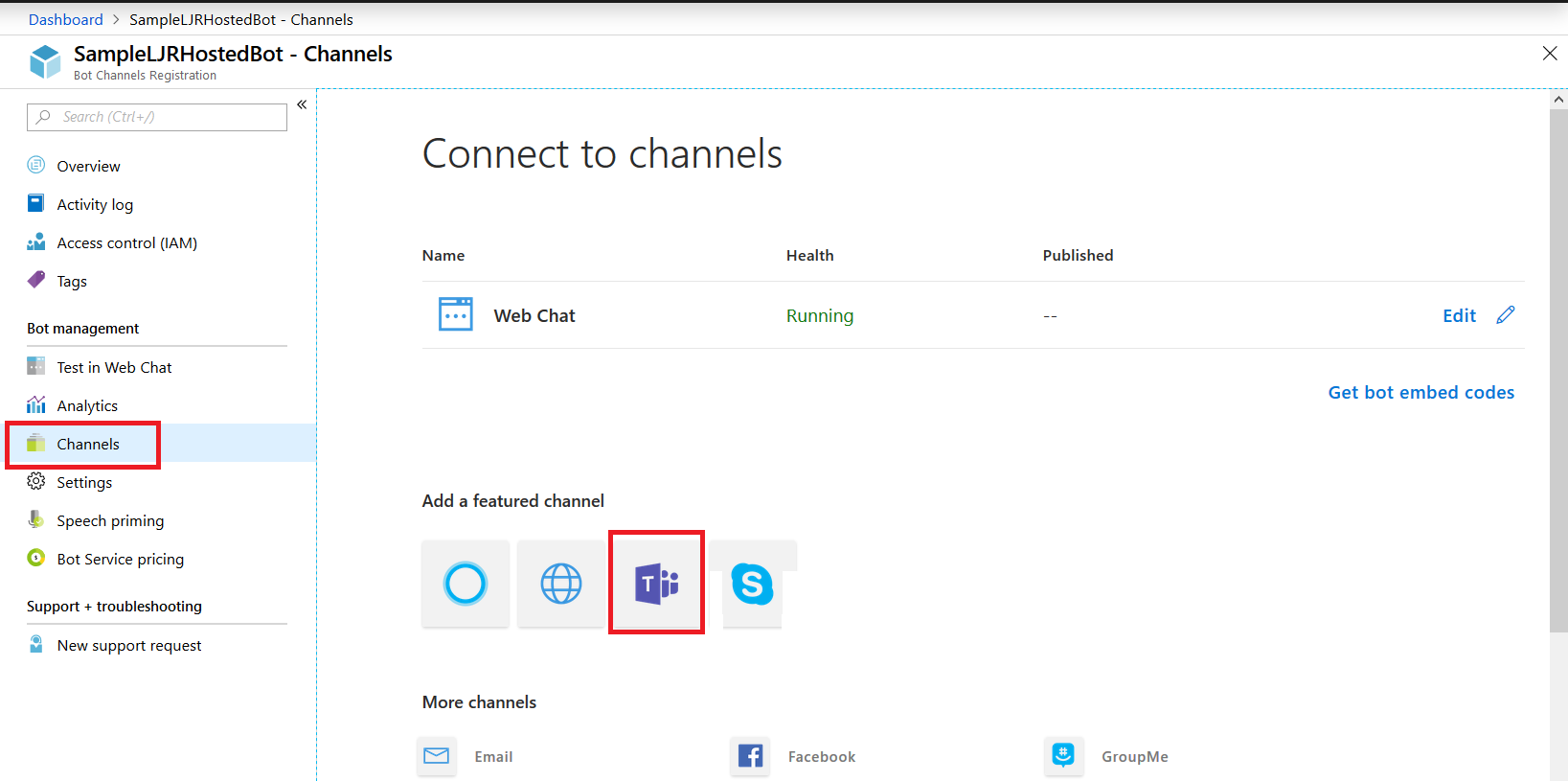
Once the channel has been created, click on the “Get bot embed codes” hyperlink to obtain the bot URL.
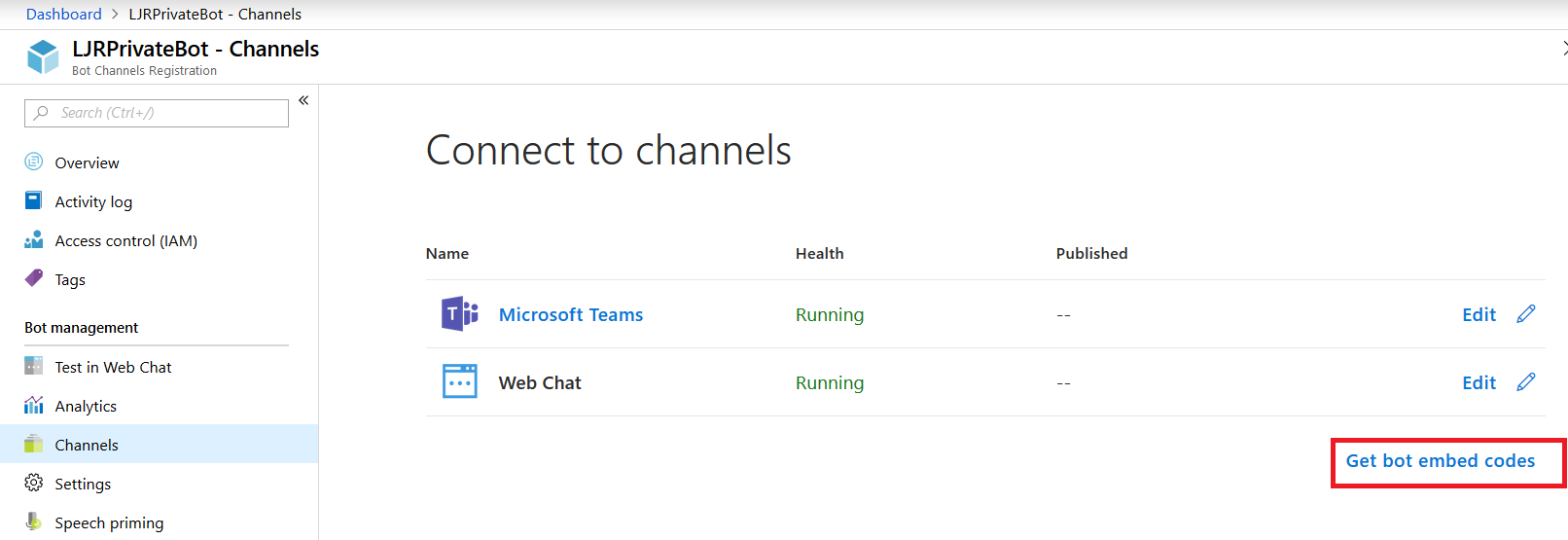
Individuals can use the hyperlink provided to add your bot to their Teams chat.
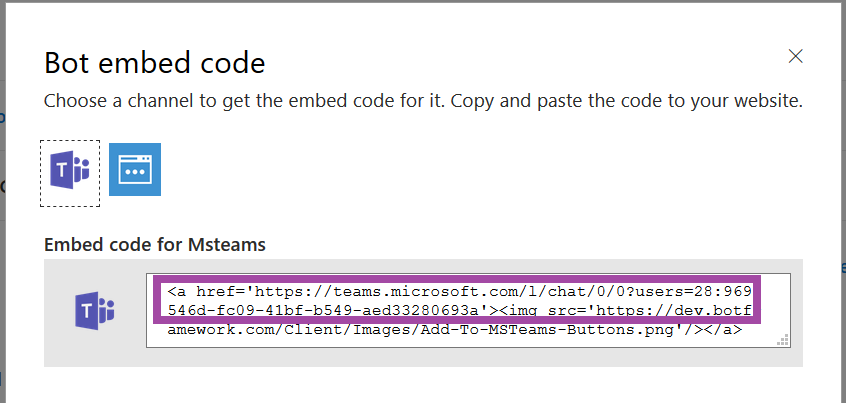
Ok, done! Except for one little thing – you need something to answer on that endpoint we entered earlier. You need a bot! Microsoft publishes an SDK and tools for building your bot in .NET, JavaScript, Python, and Java.
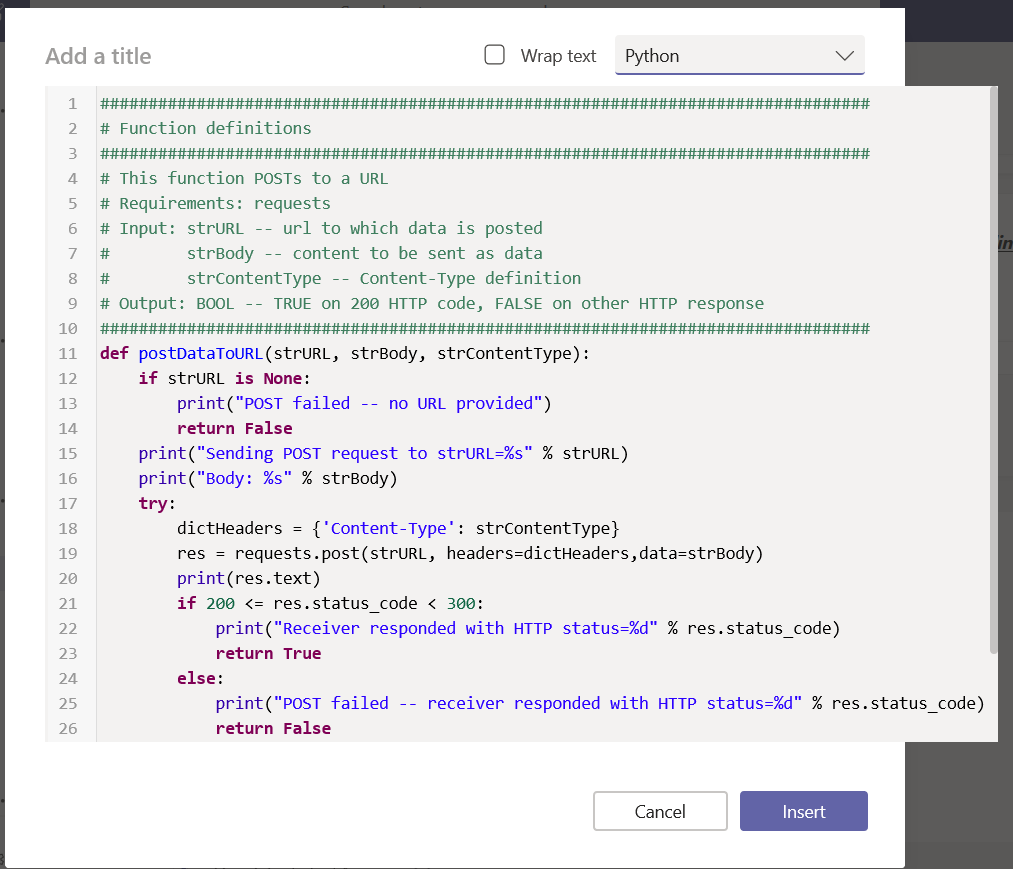
In this example, I am using a sample Python bot. For convenience, I am handling SSL on my reverse proxy instead of using an ssl wrapper in my Python service. Grab the BotBuilder package from git (https://github.com/Microsoft/botbuilder-python.git)
Install the stuff:
pip3 install -e ./libraries/botframework-connector
pip3 install -e ./libraries/botbuilder-schema
pip3 install -e ./libraries/botbuilder-core
pip3 install -r ./libraries/botframework-connector/tests/requirements.txt
In the ./samples/ folder, you’ll find a few beginner bots. Rich-Cards-Bot requires msrest that has some async functionality and the branch in requirements.txt doesn’t exist. Tried a few others and never got anything that worked properly. Same problem with EchoBot-with-State. I am using Echo-Connector-Bot because it doesn’t have this msrest problem, and I can add my own state support later.
Edit main.py and add your Azure bot application id & secret to APP_ID and APP_PASSWORD
APP_ID = ”
APP_PASSWORD = ”
PORT = 9000
SETTINGS = BotFrameworkAdapterSettings(APP_ID, APP_PASSWORD)
ADAPTER = BotFrameworkAdapter(SETTINGS)
I stash my personal information in a config.py file and added an import to main.py:
from config import strDBHostname, strDBUserName, strDBPassword, strDBDatabaseName, strDBTableName, APP_ID, APP_PASSWORD
Tweak the code however you want – add natural language processing, make database connections to internal resources to determine responses, make calls to internal web APIs. I also added console output so I could debug bot operations.
When you’ve completed your changes, launch your bot by running “python main.py”
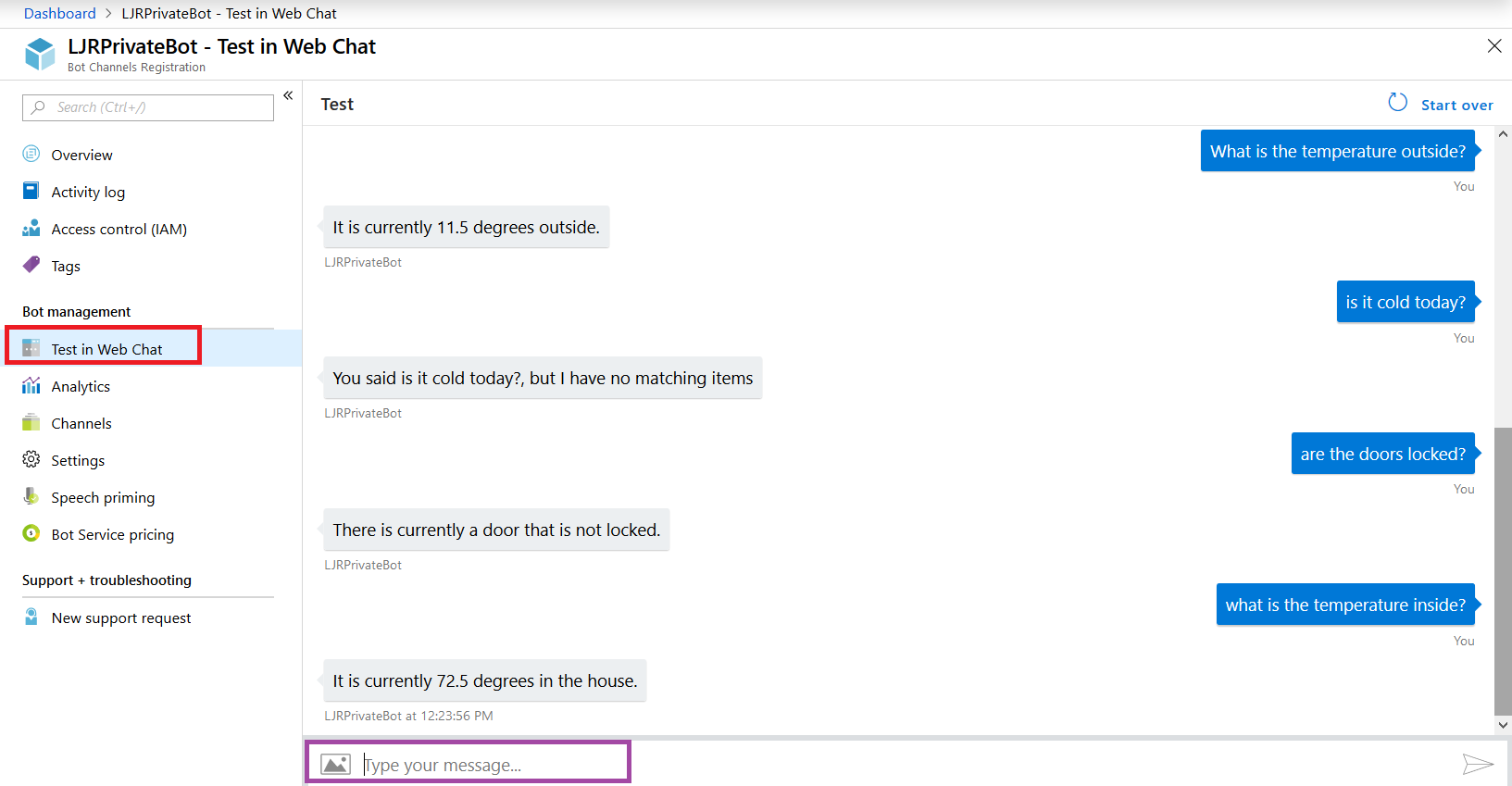
Now return to the Azure portal and select “Test in Web Chat” – this will allow you to test interactions with your bot. Ask questions – you should see your answers returned.
Once you confirm the bot is functioning properly, use the URL from the Teams channel to interact with your bot within Teams —
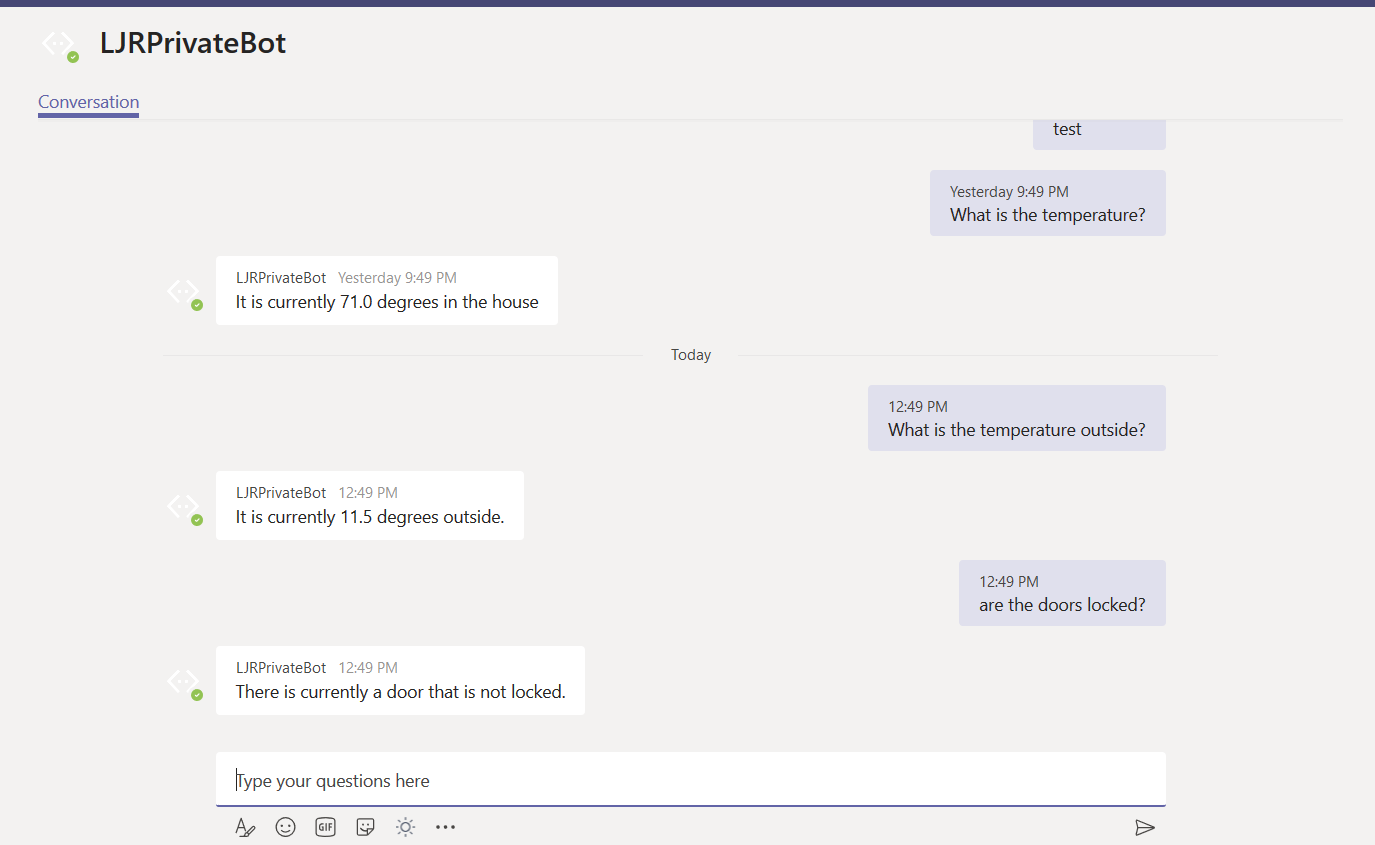
URL for my bot in Teams: https://teams.microsoft.com/l/chat/0/0?users=28:9699546d-fc09-41bf-b549-aed33280693a
The answer is served out of our home automation database – data that is only accessible on our private network.
Security – as I said earlier, you’ll probably want to take some measures to ensure access to your locally hosted bot is coming from legit sources. The app ID and secret provide one level of protection. If a connection does not supply the proper app ID & secret (or if you’ve mis-entered those values in your code!), you’ll get a 401 error.
But I don’t want the entire Internet DDoS’ing by bot either, and there is no reason for anyone outside of Microsoft Azure subnets should be accessing my locally hosted bot. My bot is hosted in a private container. The reverse proxy allows Internet-sourced traffic in to the private bot resource. Since communication from Azure will be sourced from a known set of networks, you can add a source IP restriction that prevents the general public from accessing your bot directly. See https://azurerange.azurewebsites.net/ for a convenient-to-use list of addresses.