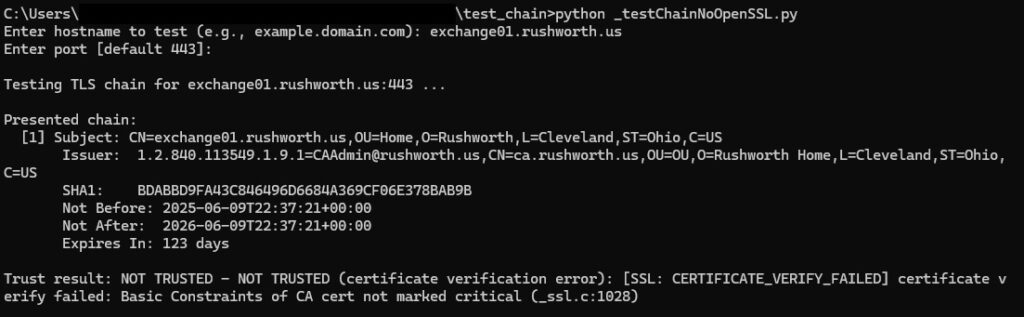
Browsers implement AIA which “helps” by repairing the certificate chain and forming a trust even without proper server configuration. Which is great for user experience, but causes a lot of challenges to people troubleshooting SSL connection failures from devices, old equipment, etc. It’s fine when I try it from my laptop!
This python script reports on the real certificate chain being served from an endpoint. Self-signed certificates will show as untrusted
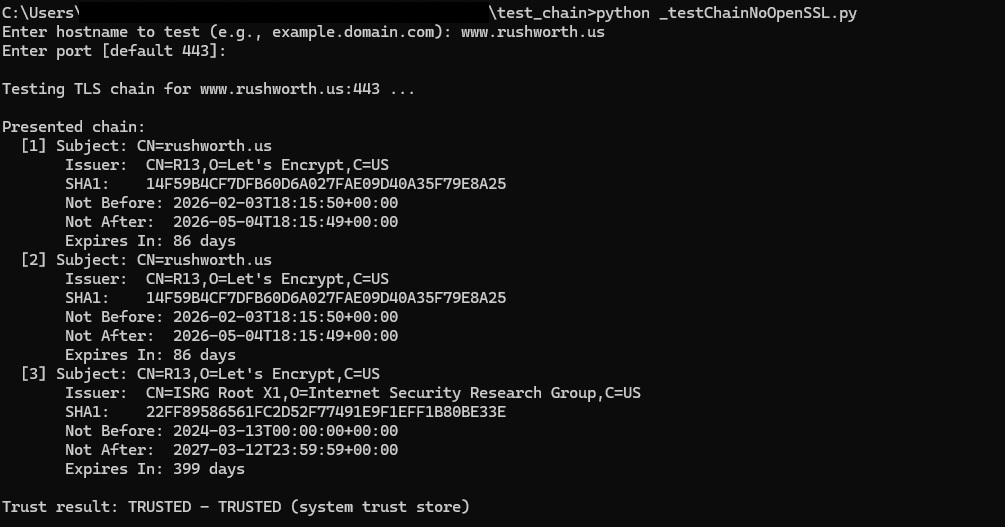
And public certs will show the chain and show as trusted
Code:
import ssl
import socket
import datetime
import select
# Third-party modules (install: pip install pyopenssl cryptography)
try:
from OpenSSL import SSL, crypto
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
except ImportError as e:
raise SystemExit(
"Missing required modules. Please install:\n"
" pip install pyopenssl cryptography\n"
f"Import error: {e}"
)
def prompt(text, default=None):
s = input(text).strip()
return s if s else default
def check_trust(hostname: str, port: int, timeout=6.0):
"""
Attempt a TLS connection using system trust store and hostname verification.
Returns (trusted: bool, message: str).
"""
try:
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
with socket.create_connection((hostname, port), timeout=timeout) as sock:
with ctx.wrap_socket(sock, server_hostname=hostname) as ssock:
# Minimal HTTP GET to ensure we fully complete the handshake
req = f"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: {hostname}\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n"
ssock.sendall(req.encode("utf-8"))
_ = ssock.recv(1)
return True, "TRUSTED (system trust store)"
except ssl.SSLCertVerificationError as e:
return False, f"NOT TRUSTED (certificate verification error): {e}"
except ssl.SSLError as e:
return False, f"NOT TRUSTED (SSL error): {e}"
except Exception as e:
return False, f"Error connecting: {e}"
def _aware_utc(dt: datetime.datetime) -> datetime.datetime:
"""
Ensure a datetime is timezone-aware in UTC. cryptography returns naive UTC datetimes.
"""
if dt.tzinfo is None:
return dt.replace(tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc)
return dt.astimezone(datetime.timezone.utc)
def _cert_to_info(cert: x509.Certificate):
subj = cert.subject.rfc4514_string()
issr = cert.issuer.rfc4514_string()
fp_sha1 = cert.fingerprint(hashes.SHA1()).hex().upper()
nb = _aware_utc(cert.not_valid_before_utc)
na = _aware_utc(cert.not_valid_after_utc)
now = datetime.datetime.now(datetime.timezone.utc)
delta_days = max(0, (na - now).days)
return {
"subject": subj,
"issuer": issr,
"sha1": fp_sha1,
"not_before": nb,
"not_after": na,
"days_to_expiry": delta_days
}
def _do_handshake_blocking(conn: SSL.Connection, sock: socket.socket, timeout: float):
"""
Drive the TLS handshake, handling WantRead/WantWrite by waiting with select.
"""
deadline = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=timeout)
while True:
try:
conn.do_handshake()
return
except SSL.WantReadError:
remaining = (deadline - datetime.datetime.now()).total_seconds()
if remaining <= 0:
raise TimeoutError("TLS handshake timed out (WantRead)")
r, _, _ = select.select([sock], [], [], remaining)
if not r:
raise TimeoutError("TLS handshake timed out (WantRead)")
continue
except SSL.WantWriteError:
remaining = (deadline - datetime.datetime.now()).total_seconds()
if remaining <= 0:
raise TimeoutError("TLS handshake timed out (WantWrite)")
_, w, _ = select.select([], [sock], [], remaining)
if not w:
raise TimeoutError("TLS handshake timed out (WantWrite)")
continue
def fetch_presented_chain(hostname: str, port: int, timeout: float = 12.0):
"""
Capture the presented certificate chain using pyOpenSSL.
Returns (chain: list of {subject, issuer, sha1, not_before, not_after, days_to_expiry}, error: str or None).
"""
# TCP connect
try:
sock = socket.create_connection((hostname, port), timeout=timeout)
sock.settimeout(timeout)
except Exception as e:
return [], f"Error connecting: {e}"
try:
# TLS client context
ctx = SSL.Context(SSL.TLS_CLIENT_METHOD)
# Compatibility tweaks:
# - Lower OpenSSL security level
try:
ctx.set_cipher_list(b"DEFAULT:@SECLEVEL=1")
except Exception:
pass
# - Disable TLS 1.3 and set minimum TLS 1.2
try:
ctx.set_options(SSL.OP_NO_TLSv1_3)
except Exception:
pass
try:
# Ensure TLSv1.2+ (pyOpenSSL exposes set_min_proto_version on some builds)
if hasattr(ctx, "set_min_proto_version"):
ctx.set_min_proto_version(SSL.TLS1_2_VERSION)
except Exception:
pass
# - Set ALPN to http/1.1 (some paths work better when ALPN is present)
try:
ctx.set_alpn_protos([b"http/1.1"])
except Exception:
pass
conn = SSL.Connection(ctx, sock)
conn.set_tlsext_host_name(hostname.encode("utf-8"))
conn.set_connect_state()
# Blocking mode (best effort)
try:
conn.setblocking(True)
except Exception:
pass
# Drive handshake
_do_handshake_blocking(conn, sock, timeout=timeout)
# Retrieve chain (some servers only expose leaf)
chain = conn.get_peer_cert_chain()
infos = []
if chain:
for c in chain:
der = crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_ASN1, c)
cert = x509.load_der_x509_certificate(der)
infos.append(_cert_to_info(cert))
else:
peer = conn.get_peer_certificate()
if peer is not None:
der = crypto.dump_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_ASN1, peer)
cert = x509.load_der_x509_certificate(der)
infos.append(_cert_to_info(cert))
# Cleanup
try:
conn.shutdown()
except Exception:
pass
finally:
try:
conn.close()
except Exception:
pass
try:
sock.close()
except Exception:
pass
if not infos:
return [], "No certificates captured (server did not present a chain and peer cert unavailable)"
return infos, None
except Exception as e:
try:
sock.close()
except Exception:
pass
etype = type(e).__name__
emsg = str(e) or "no message"
return [], f"TLS handshake or chain retrieval error: {etype}: {emsg}"
def main():
hostname = prompt("Enter hostname to test (e.g., example.domain.com): ")
if not hostname:
print("Hostname is required.")
return
port_str = prompt("Enter port [default 443]: ", "443")
try:
port = int(port_str)
except ValueError:
print("Invalid port.")
return
print(f"\nTesting TLS chain for {hostname}:{port} ...")
chain, err = fetch_presented_chain(hostname, port)
print("\nPresented chain:")
if err:
print(f" [ERROR] {err}")
elif not chain:
print(" [No certificates captured]")
else:
for i, ci in enumerate(chain, 1):
print(f" [{i}] Subject: {ci['subject']}")
print(f" Issuer: {ci['issuer']}")
print(f" SHA1: {ci['sha1']}")
nb_val = ci.get("not_before")
na_val = ci.get("not_after")
nb_str = nb_val.isoformat() if isinstance(nb_val, datetime.datetime) else str(nb_val)
na_str = na_val.isoformat() if isinstance(na_val, datetime.datetime) else str(na_val)
print(f" Not Before: {nb_str}")
print(f" Not After: {na_str}")
dte = ci.get("days_to_expiry")
if dte is not None:
print(f" Expires In: {dte} days")
trusted, msg = check_trust(hostname, port)
print(f"\nTrust result: {'TRUSTED' if trusted else 'NOT TRUSTED'} - {msg}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
