We had a Postgres server go into read-only mode — which provided a stressful opportunity to learn more nuances of Postgres internals. It appears this “read only mode” something Postgres does to save it from itself. Transaction IDs are assigned to each row in the database — the ID values are used to determine what transactions can see. For each transaction, Postgres increments the last transaction ID and assigns the incremented value to the current transaction. When a row is written, the transaction ID is stored in the row and used to determine whether a row is visible to a transaction.
Inserting a row will assign the last transaction ID to the xmin column. A transaction can see all rows where xmin is less than its transaction ID. Updating a row actually creates a new row — the old row then has an xmax value and the new row has the same number as its xmin — transactions with IDs newer than the xmax value will not see the row. Similarly, deleting a row updates the row’s xmax value — older transactions will still be able to see the row, but newer ones will not.
You can even view the xmax and xmin values by specifically asking for them in a select statement: select *, xmin, xmax from TableName;
The transaction ID is stored in a 32-bit number — making the possible values 0 through 4,294,967,295. Which can become a problem for a heavily I/O or long-running database (i.e. even if I only get a couple of records an hour, that adds up over years of service) because … what happens when we get to 4,294,967,295 and need to write another record? To combat this, Postgres does something that reminds me of the “doomsday” Mayan calendar — this number range isn’t aligned on a straight line where one eventually runs into a wall. The numbers are arranged in a circle, so there’s always a new cycle and numbers are issued all over again. In the Postgres source, the wrap limit is “where the world ends”! But, like the Mayan calendar … this isn’t actually the end as much as it’s a new beginning.
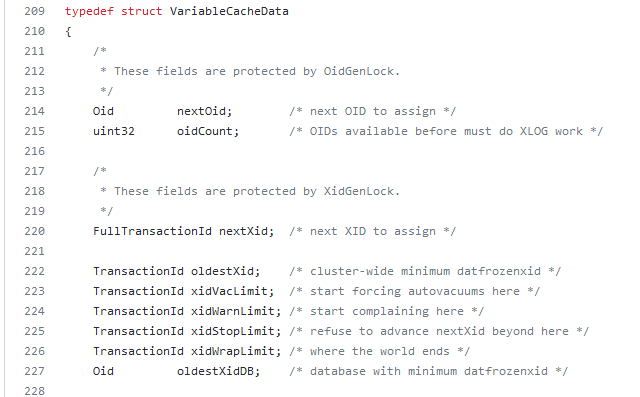
How do you know if transaction 5 is ‘old’ or ‘new’ if the number can be reissued? The database considers half of the IDs in the real past and half for future use. When transaction ID four billion is issued, ID number 5 is considered part of the “future”; but when the current transaction ID is one billion, ID number 5 is considered part of the “past”. Which could be problematic if one of the first records in the database has never been updated but is still perfectly legitimate. Reserving in-use transaction IDs would make the re-issuing of transaction IDs more resource intensive (not just assign ++xid to this transaction, but xid++;is xid assigned {if so, xid++ and check again until the answer is no}; assign xid to this transaction). Instead of implementing more complex logic, rows can be “frozen” — this is a special flag that basically says “I am a row from the past and ignore my transaction ID number”. In versions 9.4 and later, both committed and aborted hint bits are set to freeze a row — in earlier versions, used a special FrozenTransactionId index.
There is a minimum age for freezing a row — it generally doesn’t make sense to mark a row that’s existed for eight seconds as frozen. This is configured in the database as the vacuum_freeze_min_age. But it’s also not good to let rows sit around without being frozen for too long — the database could wrap around to the point where the transaction ID is reissued and the row would be lost (well, it’s still there but no one can see it). Since vacuuming doesn’t look through every page of the database on every cycle, there is a vacuum_freeze_table_age which defines the age of a transaction where vacuum will look through an entire table to freeze rows instead of relying on the visibility map. This combination, hopefully, balances the I/O of freezing rows with full scans that effectively freeze rows.
What I believe led to our outage — most of our data is time-series data. It is written, never modified, and eventually deleted. Auto-vacuum will skip tables that don’t need vacuuming. In our case, that’s most of the tables. The autovacuum_freeze_max_age parameter sets an ‘age’ at which vacuuming is forced. If these special vacuum processes don’t complete fully … you eventually get into a state where the server stops accepting writes in order to avoid potential data loss.
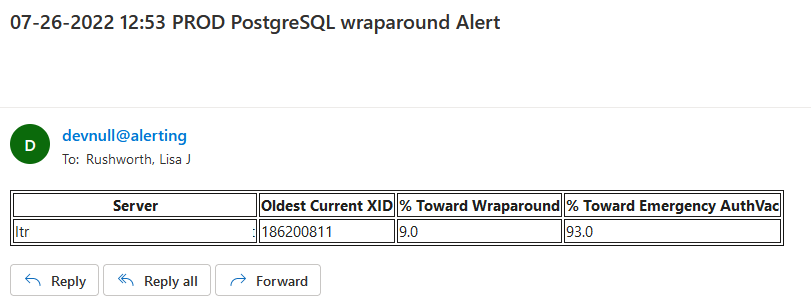
So monitoring for transaction IDs approaching the wraparound and emergency vacuum values is important. I set up a task that alerts us when we approach wraparound (fortunately, we’ve not gotten there again) as well as when we approach the emergency auto-vacuum threshold — a state which we reach a few times a week.
Using the following query, we monitor how close each of our databases is to both the auto-vacuum threshold and the ‘end of the world’ wrap-around point.
WITH max_age AS ( SELECT 2000000000 as max_old_xid
, setting AS autovacuum_freeze_max_age FROM pg_catalog.pg_settings
WHERE name = 'autovacuum_freeze_max_age' )
, per_database_stats AS ( SELECT datname , m.max_old_xid::int
, m.autovacuum_freeze_max_age::int
, age(d.datfrozenxid) AS oldest_current_xid
FROM pg_catalog.pg_database d
JOIN max_age m ON (true) WHERE d.datallowconn )
SELECT max(oldest_current_xid) AS oldest_current_xid
, max(ROUND(100*(oldest_current_xid/max_old_xid::float))) AS percent_towards_wraparound
, max(ROUND(100*(oldest_current_xid/autovacuum_freeze_max_age::float))) AS percent_towards_emergency_autovac FROM per_database_stats
If we are approaching either point, e-mail alerts are sent.
When a database approaches the emergency auto-vacuum threshold, we freeze data manually — vacuumdb --all --freeze --jobs=1 --echo --verbose --analyze (or –jobs=3 if I want the process to hurry up and get done).